Understanding the temperature rise calculation IEC 60890 is crucial for engineers and designers working with electrical enclosures. The IEC 60890 standard provides a method to estimate temperature increases inside electrical panels, ensuring safe operation and preventing overheating. This guide explains the key principles, formulas, and steps to perform accurate calculations while staying compliant.

Why Temperature Rise Calculation Matters
Electrical enclosures must dissipate heat efficiently to avoid component failure. Excessive temperature rise can lead to:
- Reduced lifespan of electrical components
- Increased risk of short circuits
- Non-compliance with safety regulations
The IEC 60890 standard offers a systematic approach to predict and control temperature rise, ensuring reliability and safety.
Key Factors in IEC 60890 Temperature Rise Calculation

1. Heat Dissipation Inside the Enclosure
The standard considers:
- Power losses from installed equipment
- Enclosure material (steel, aluminum, etc.)
- Surface area for natural cooling
2. Ambient Temperature Influence
The surrounding temperature affects internal heat buildup. The calculation adjusts for different environmental conditions.
3. Ventilation and Cooling Methods
- Natural convection (passive cooling)
- Forced ventilation (fans, air conditioning)
Step-by-Step Temperature Rise Calculation per IEC 60890

Step 1: Determine Total Power Loss (P)
Sum the heat generated by all components inside the enclosure.
Step 2: Calculate Effective Cooling Surface Area (A)
The enclosure’s surface area impacts heat dissipation.
Step 3: Apply the IEC 60890 Formula
The standard provides empirical formulas to estimate temperature rise
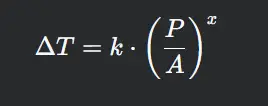
Where:
- k = Material coefficient
- x = Exponent based on enclosure type
Step 4: Verify Against Maximum Allowable Temperature
Compare the calculated ΔT with component ratings to ensure compliance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring non-uniform heat distribution
- Overlooking solar radiation effects (for outdoor enclosures)
- Incorrect material thermal conductivity values
Conclusion
Accurate temperature rise calculation IEC 60890 ensures electrical enclosures operate safely and efficiently. By following the standard’s guidelines, engineers can prevent overheating, extend equipment life, and meet regulatory requirements.
For complex installations, consider thermal simulation software for precise analysis.
IEC STANDARD DOWNLOAD